≪特徴≫
・マウス胎児由来線維芽細胞(Mouse embryonic fibroblast)です。 ・マウス、サル、ヒトES細胞、ヒトiPS細胞のフィーダー細胞として幅広くお使いいただけます。 ・全ロットで、ヒトiPS細胞による培養試験を行っておりますので、安心してお使いいただけます。 ・マイトマイシンC処理をしていますので、播種翌日からフィーダー細胞としてご使用いただけます。※保存温度:液体窒素
※当製品は温度変化に非常に敏感な製品のため、お手元に細胞が届きましたらすぐに液体窒素に保管してください。細胞を保管するまでに時間がかかってしまうと細胞の接着率が悪くなることがございますので素早く保管してください。
≪概要≫
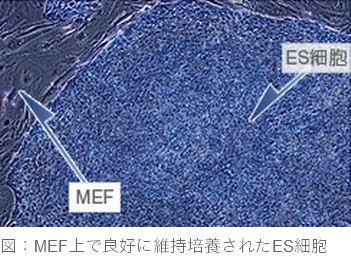
MEF(マウス胎児線維芽細胞)はES細胞やiPS細胞のフィーダー細胞として広く使用されています。図に示すように、ES細胞はMEF上で良好に維持培養されます。MEFは初代培養細胞特有のロット間差がありますが、当社のMEFは全ロットについてiPS細胞を用いた培養検定を実施しておりますので安心してお使いいただけます。当製品には詳しい使用説明書が添付しております。
プロトコル
データシート
- Lot.20181108
- Lot.20180802
- Lot.20180208
- Lot.20171214
- Lot.20171130
- Lot.20171116
- Lot.20171019
- Lot: 20170209
- Lot: 20161222
- Lot: 20160804
- Lot: 20160728
- Lot: 20160519
- Lot: 20160331
- Lot: 20160310
- Lot: 20160204
- Lot: 20160128
- Lot: 20160121
- Lot: 20151210
- Lot: 20151105
- Lot: 20151029
- Lot: 20151008
- Lot: 20150709
- Lot: 20150430
- Lot: 20150409
- Lot: 20150312
- Lot: 20150219
- Lot: 20150204
- Lot: 20150115
- Lot: 20141225
- Lot: 20141218
- Lot: 20141211
- Lot: 20141204
- Lot: 20141120
- Lot: 20141106
- Lot: 20141016
- Lot: 20141009
- Lot: 20140925
- Lot: 20140911
- Lot: 20140904
- Lot: 20140807
- Lot: 20140724
- Lot: 20140717
- Lot: 20140710
- Lot: 20140626
- Lot: 20140605
- Lot: 20140501
- Lot: 20140410
- Lot: 20140327
- Lot: 20140313
- Lot: 20140227
- Lot: 20140213
- Lot: 20140206
- Lot: 20140123
- Lot: 20140117
論文・発表
- Matsuura K, Seta H, Haraguchi Y, Alsayegh K, Sekine H, Shimizu T, Hagiwara N, Yamazaki K, Okano T. TRPV-1-mediated elimination of residual iPS cells in bioengineered cardiac cell sheet tissues. Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 18;6:21747. doi:10.1038/srep21747. PubMed PMID: 26888607.
- Chen, Ling, et al. “Mouse induced pluripotent stem cell microenvironment generates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in mouse Lewis lung cancer cells.” American journal of cancer research 4.1 (2014): 80.
- Kim, Mee‐Hae, Eri Masuda, and Masahiro Kino‐Oka. “Kinetic analysis of deviation from the undifferentiated state in colonies of human induced pluripotent stem cells on feeder layers.” Biotechnology and bioengineering (2014).
- Haraguchi, Yuji, et al. “Simple suspension culture system of human iPS cells maintaining their pluripotency for cardiac cell sheet engineering.” Journal of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine (2013).
- Sugimoto, Kouji, et al. “Effects of hypoxia on pluripotency in murine iPS cells.” Microscopy research and technique 76.10 (2013): 1084-1092.
- Chen, Ling, et al. “A model of cancer stem cells derived from mouse induced pluripotent stem cells.” PLoS One 7.4 (2012): e33544.
- Fukushima, H., et al. “SSEA-4 is a marker of human deciduous periodontal ligament stem cells.” Journal of dental research 91.10 (2012): 955-960.
- Imai, Koichi, et al. “In vitro study of cell differentiation by two type mouse embryo stem cells on mono-and multilayer nanocarbon tubes.” Applied Surface Science 258.22 (2012): 8444-8447.
- Ishikawa, Tetsuya, Keitaro Hagiwara, and Takahiro Ochiya. “Generation and hepatic differentiation of human iPS cells.” Liver Stem Cells. Springer New York, (2012). 103-114.
- Masuda, Shigeo, et al. “A simplified in vitro teratoma assay for pluripotent stem cells injected into rodent fetal organs.” Cell Medicine 3.1-3 (2012): 1-3.
- IMAI, Koichi, et al. “An Attempt to Cell Differentiation in Three-dimensional Culture System Using Non-feeder ES-D3 Cells and Feeder Layer Type ES cells.” Journal of Oral Tissue Engineering 8.3 (2011): 203-211.
- Inamura, Mitsuru, et al. “Efficient generation of hepatoblasts from human ES cells and iPS cells by transient overexpression of homeobox gene HEX.” Molecular Therapy 19.2 (2011): 400-407.
- Kobayashi, Hideyuki. “Pluripotent Stem Cells Induced from Testicular Tissue of a Man with Klinefelter Syndrome (47, XXY) by Four Transcription Factors (OCT4, SOX2, KLF4, and C-MYC).” (2011).
- Kobayashi, Hideyuki, et al. “Reprogramming of adult human testicular cells by four transcription factors (OCT4, SOX2, KLF4, and C-MYC).” Reproductive medicine and biology 10.2 (2011): 105-112.
- Sakai, Y., and K. Nakazawa. “Novel Microchip Technique for the Transfer of Spheroids as Floating Cultures to Micropatterned-Adherent Cultures.” J Biochip Tissue chip S 4 (2011): 2153-0777.
- Sakai, Yusuke, Yukiko Yoshiura, and Kohji Nakazawa. “Embryoid body culture of mouse embryonic stem cells using microwell and micropatterned chips.” Journal of bioscience and bioengineering 111.1 (2011): 85-91.
- Oka, Y., et al. “293FT cells transduced with four transcription factors (OCT4, SOX2, NANOG, and LIN28) generate aberrant ES-like cells.” J Stem cell Regenerative Med 3 (2010): 149-56.
- Lee, Tae-Hee, et al. “Functional recapitulation of smooth muscle cells via induced pluripotent stem cells from human aortic smooth muscle cells.”Circulation research 106.1 (2010): 120-128.
- Sakai, Yusuke, et al. “Effect of microwell chip structure on cell microsphere production of various animal cells.” Journal of bioscience and bioengineering110.2 (2010): 223-229.